🔒 Denial of Wallet Attack – Complete Guide
1. Definition
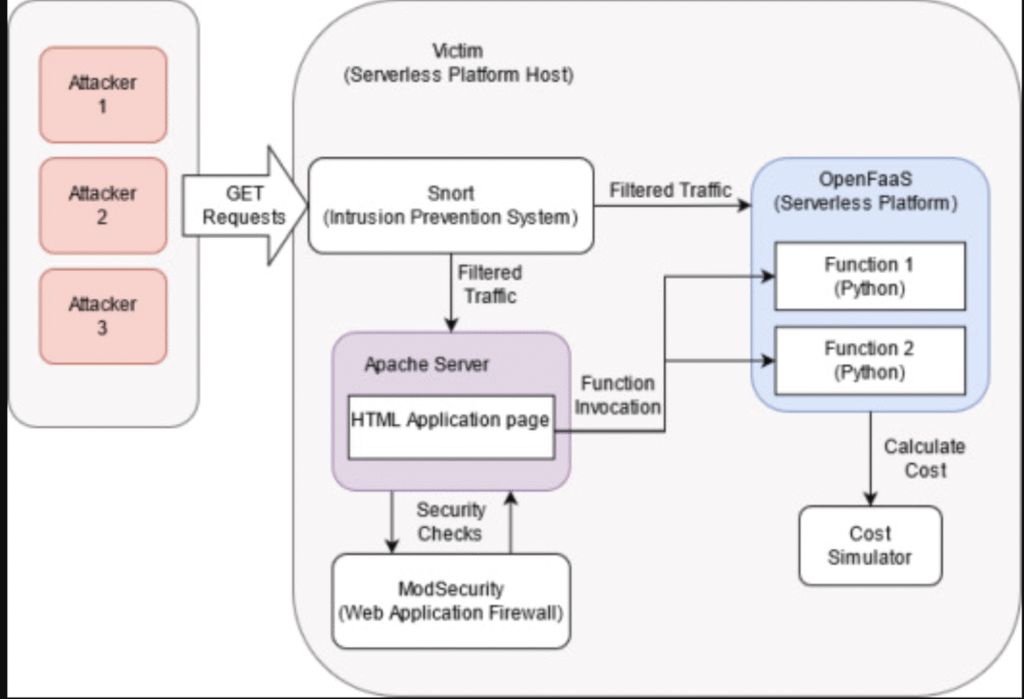
A Denial of Wallet (DoW) attack is a type of cloud-specific denial-of-service (DoS) attack where the attacker doesn’t just try to exhaust system resources, but instead forces the victim to consume paid cloud resources, inflating costs until the service becomes financially unsustainable.
Unlike traditional DoS/DDoS attacks that target availability, DoW attacks exploit the “pay-per-use” billing model of cloud services.
2. How it Works
- Target: A cloud-hosted application or API that scales automatically (serverless, containers, PaaS).
- Exploit: Attacker repeatedly sends valid requests, often small or cheap individually.
- Consequence: The cloud provider auto-scales resources to serve them, racking up costs for the victim.
- Outcome: Even if the system doesn’t crash, the bill skyrockets, causing economic denial of service.
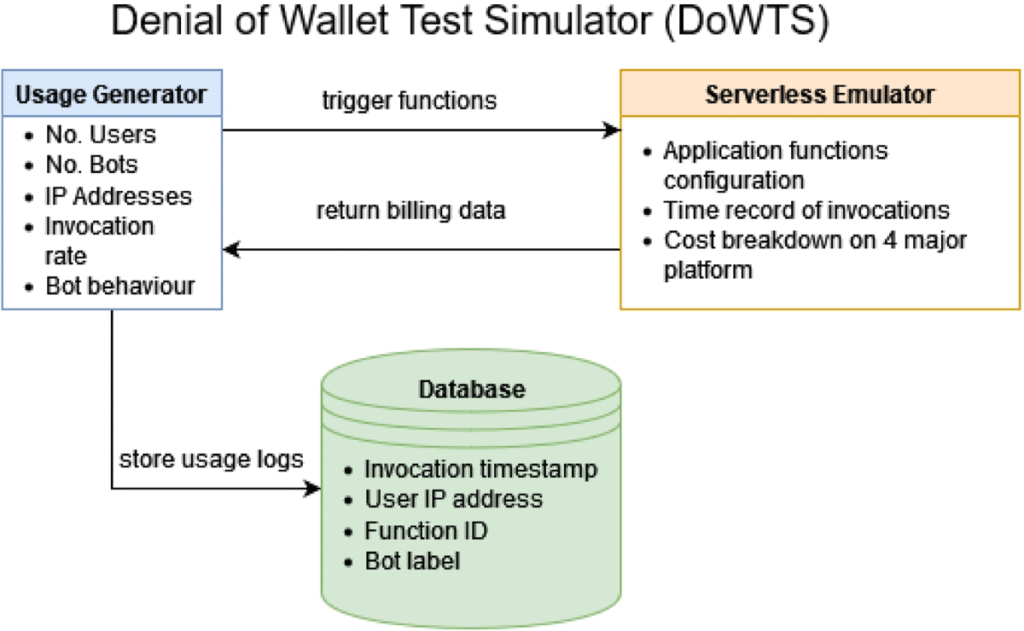
3. Key Characteristics
- Focuses on cost escalation, not just downtime.
- Exploits auto-scaling and pay-as-you-go pricing models.
- Can be harder to detect since requests may look “legitimate.”
4. Use Cases (Attacker’s Perspective)
- Targeting startups: Force small companies to abandon services by inflating cloud costs.
- API abuse: Mass requests to public APIs that charge per request.
- Serverless exploitation: Triggering excessive AWS Lambda / Google Cloud Functions executions.
- Data egress abuse: Downloading/forcing large amounts of outbound bandwidth (expensive in cloud).
- AI/ML inference APIs: Triggering repeated, costly inference runs.
5. Real-World Example
- An attacker floods an image recognition API hosted on AWS Lambda.
- The API auto-scales to handle the load.
- Each request costs $0.0001, but millions of requests = thousands of dollars in minutes.
- The system works perfectly (no downtime) → but the bill destroys the victim’s wallet.
6. Defense & Mitigation Strategies
✅ Rate Limiting & Throttling
- Limit requests per user/IP/token.
- Protect APIs using WAF (Web Application Firewall).
✅ Budgets & Alerts
- Set billing alarms in AWS, GCP, Azure.
- Automatically shut down services after exceeding thresholds.
✅ Usage Quotas
- Implement quotas at the app-level (e.g., “1000 requests/day per user”).
✅ CAPTCHA & AuthN
- Protect free/public endpoints with authentication or CAPTCHA challenges.
✅ Egress Controls
- Limit data transfer (since outbound bandwidth is expensive).
✅ Anomaly Detection
- Monitor for sudden spikes in usage that don’t match business activity.
7. Tools & Frameworks
Here are some tools and cloud-native features to defend against Denial of Wallet attacks:
🔹 Cloud Provider Features
- AWS:
- AWS WAF
- AWS Budgets & Billing Alarms
- API Gateway throttling
- Azure:
- Azure Monitor & Cost Alerts
- API Management quotas
- GCP:
- Google Cloud Armor
- Quota limits & budget notifications
🔹 Open Source & Security Tools
- OWASP Defenders: API Security project guidelines.
- Kong / NGINX API Gateway: Rate limiting plugins.
- Istio / Envoy: Service mesh with quotas & rate limits.
- Fail2Ban: Blocks abusive IPs at the network level.
8. Tutorial – Protecting Against DoW (Example with AWS API Gateway)
- Create an API in AWS API Gateway.
- Go to Method Request → Enable API Keys Required.
- Under Usage Plans → Define Rate (requests/second) and Quota (total requests/day).
- Attach WAF rules to block common attack patterns.
- In AWS Budgets, create a budget alert for unexpected billing spikes.
- Monitor in CloudWatch for anomalies.
Now your API won’t scale infinitely and charge you a fortune.
9. Summary
- Denial of Wallet = Cloud-specific attack that targets your wallet instead of your servers.
- Exploits auto-scaling & pay-per-use pricing models.
- Defenses involve rate limiting, quotas, billing alarms, and anomaly detection.
- Must be part of cloud security posture for startups and enterprises alike.